Difference between revisions of "Week Eight (MGDP2050)"
Karl Jones (Talk | contribs) (→Browse sample components) |
Karl Jones (Talk | contribs) (→Instructor's example: JavaScript) |
||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
[[File:JQuery-UI-example-css.gif]] | [[File:JQuery-UI-example-css.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Instructor's example: HTML for link === | ||
| + | |||
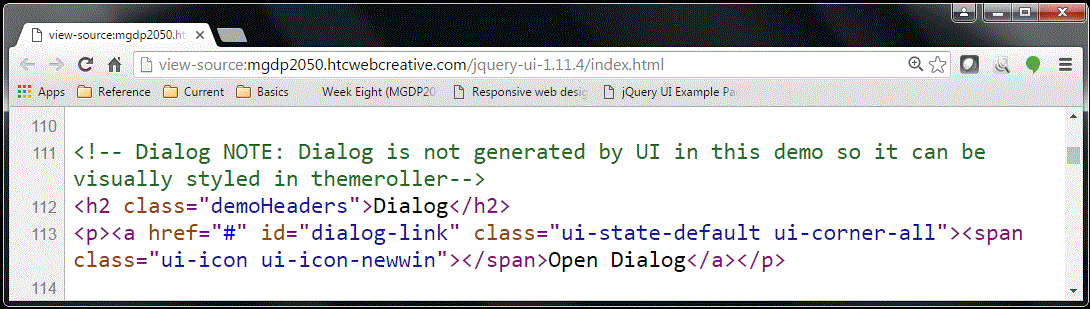
| + | The screenshot below shows the HTML for the link that launches the Dialog component: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:JQuery-UI-example-html-link.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Instructor's example: HTML for Dialog === | ||
| + | |||
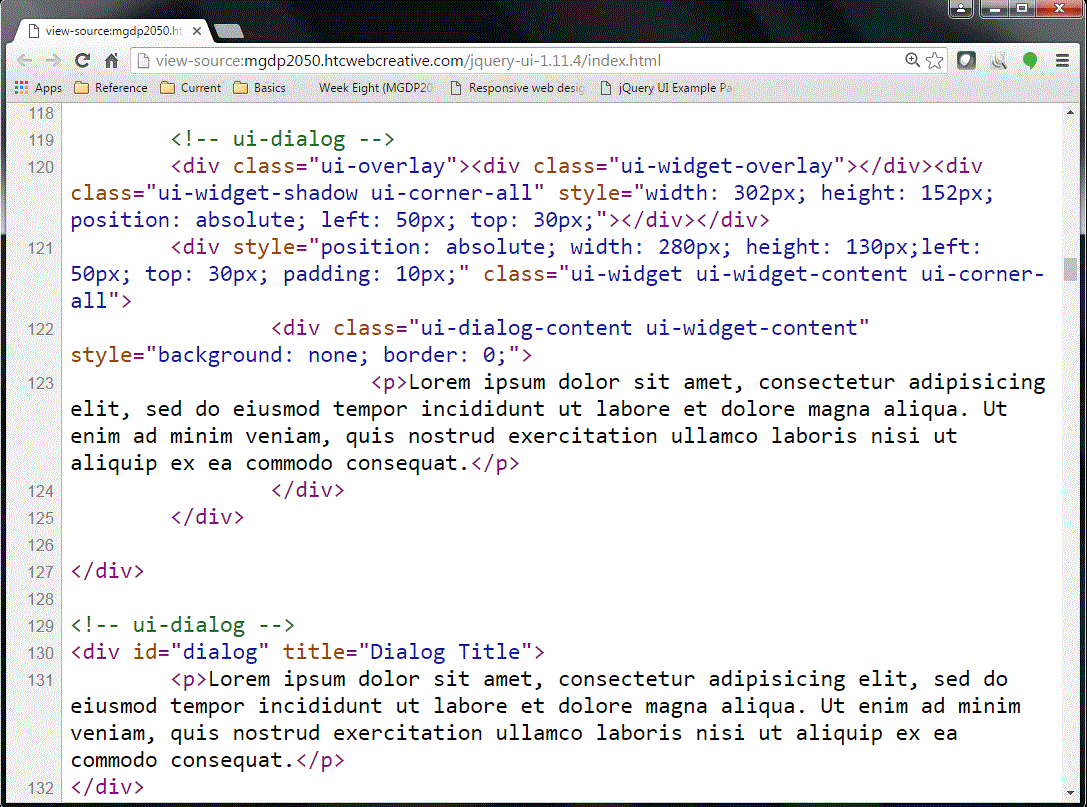
| + | The screenshot below shows the HTML for the Dialog itself: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:JQuery-UI-example-html-dialog.gif]] | ||
=== Instructor's example: JavaScript === | === Instructor's example: JavaScript === | ||
Revision as of 07:42, 29 March 2016
Lecture notes and exercises for Week Eight of Web Design and Development II (MGDP2050).
See also Week Seven (MGDP2050) - Week Nine (MGDP2050).
Contents
- 1 HTML and semantics
- 2 Semantic HTML
- 3 Bold versus strong
- 4 Italic versus emphasis
- 5 JavaScript
- 6 jQuery
- 7 jQuery UI
- 8 Exercises: in class
- 9 Browse the jQuery UI demos
- 9.1 Download and install jQuery UI
- 9.2 Instructor's example: components
- 9.3 Instructor's example
- 9.4 Instructor's example: CSS
- 9.5 Instructor's example: HTML for link
- 9.6 Instructor's example: HTML for Dialog
- 9.7 Instructor's example: JavaScript
- 9.8 Instructor's example: Dialog component screenshot
- 9.9 Instructor's example: Dialog component text
- 9.10 Create folder named week8
- 9.11 Create web page
- 9.12 Demonstrate a jQuery UI component
- 9.13 Update your home page
- 9.14 Upload to web server
- 10 Exercises: for next week
- 11 Reading for next week
HTML and semantics
In principle, the role of HTML is to provide semantics (meaning).
In practice, HTML is a mix of semantic and non-semantic elements.
Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML refers to HTML that is entirely semantic (or perhaps "very semantic with acceptable compromises").
Bold versus strong
Earlier versions of HTML specified a bold element, to make text display in boldface.
HTML 4 also specified a strong element, intended to replace the bold element.
Both elements are valid in HTML5.
Italic versus emphasis
Earlier versions of HTML specified an italic element, to make text display in italicf.
HTML 4 also specified an emphasis element, intended to replace the italic element.
Both elements are valid in HTML5.
JavaScript
Recognizing JavaScript
Using JavaScript
Script element
- Use the script element to include JavaScript in a web page.
Debugging JavaScript
- See the browser console for JavaScript error messages and other browser-related tools.
JavaScript Validation
jQuery
- Review jQuery ...
jQuery UI
Introduce jQuery UI ...
Exercises: in class
Browse the jQuery UI demos
Browse the jQuery UI demos.
Try several.
Pick three which interest you.
Download and install jQuery UI
Browse the jQuery UI website:
Click the "Stable" link (in the Quick Downloads section).
- This will download a Zip file containing the jQuery UI files.
Unzip the Zip file, if necessary, to get the jQuery UI folder.
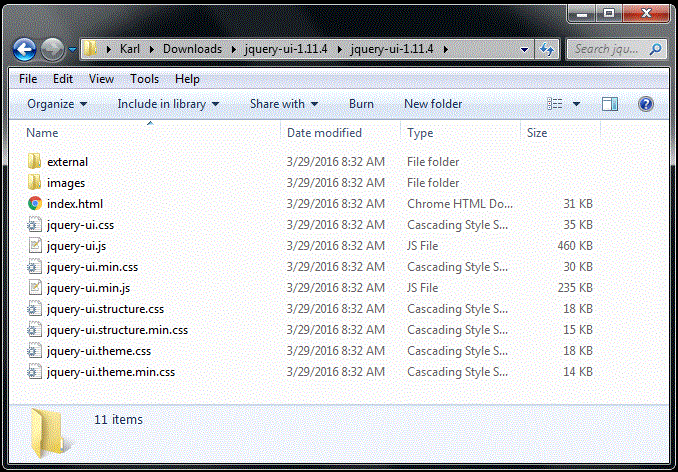
There is a first folder named jquery-ui-1.11.4 (or something similar -- version number may increase).
This folder contains a second folder with the same name, containing the jQuery UI files and subfolders. This is the actual jQuery UI folder.
Screenshot:
Move the jQuery UI folder to your local root folder.
You can now use jQuery UI in your web pages.
Instructor's example: components
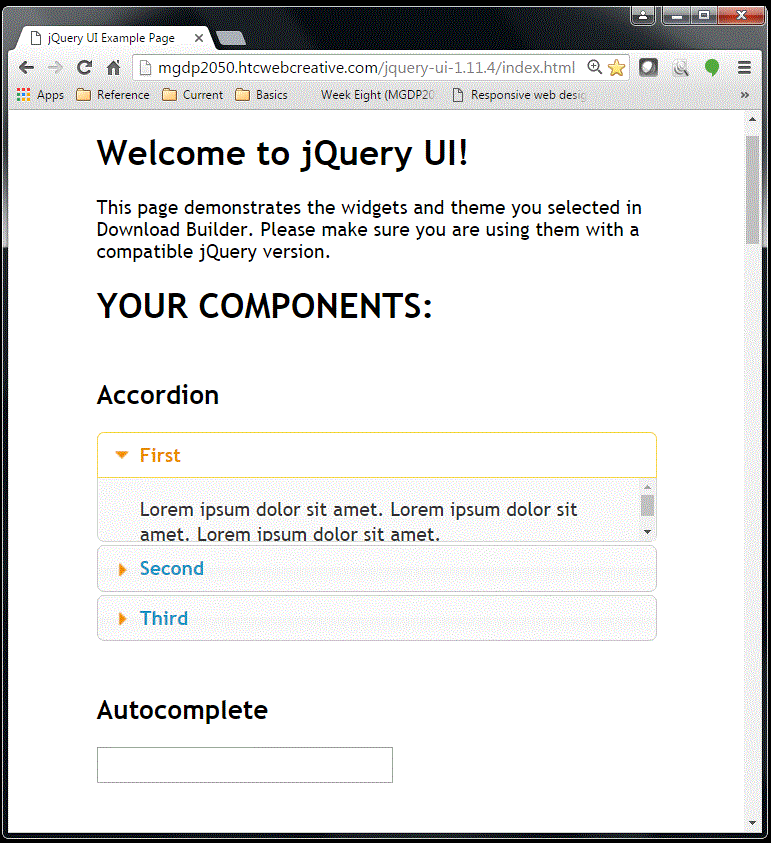
The jQuery UI folder contains a web page named index.html which demonstrates the components.
The screeshot below shows the components page in a web browser:
Instructor's example
Sample components page, instructor's example:
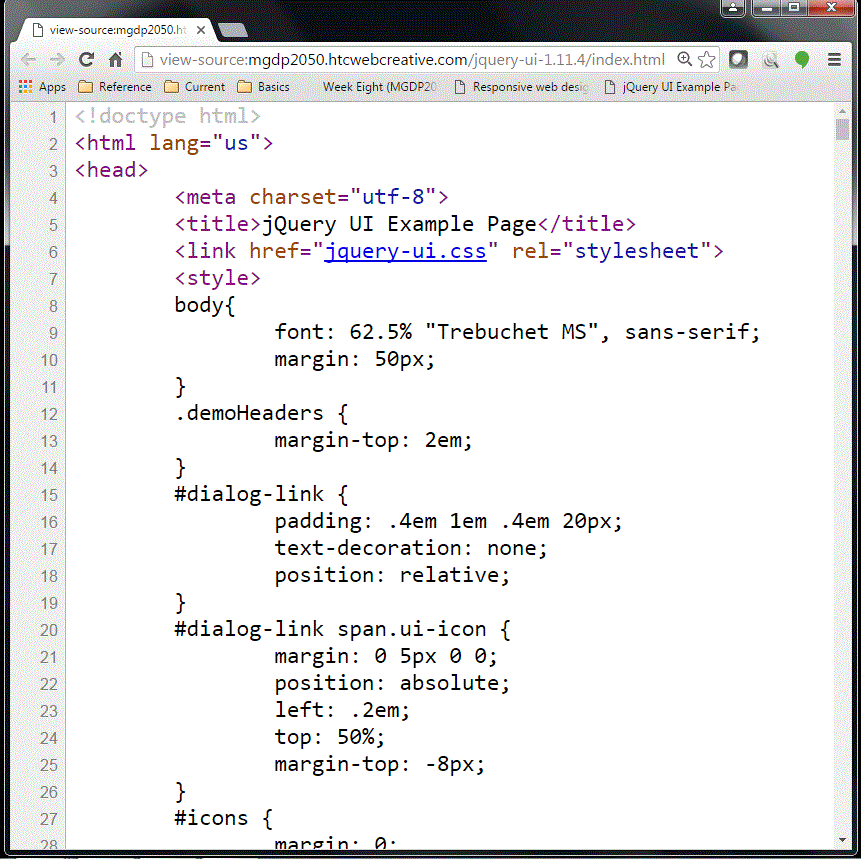
Instructor's example: CSS
Screenshot of source code -- note the external CSS file, and the internal CSS styles:
Instructor's example: HTML for link
The screenshot below shows the HTML for the link that launches the Dialog component:
Instructor's example: HTML for Dialog
The screenshot below shows the HTML for the Dialog itself:
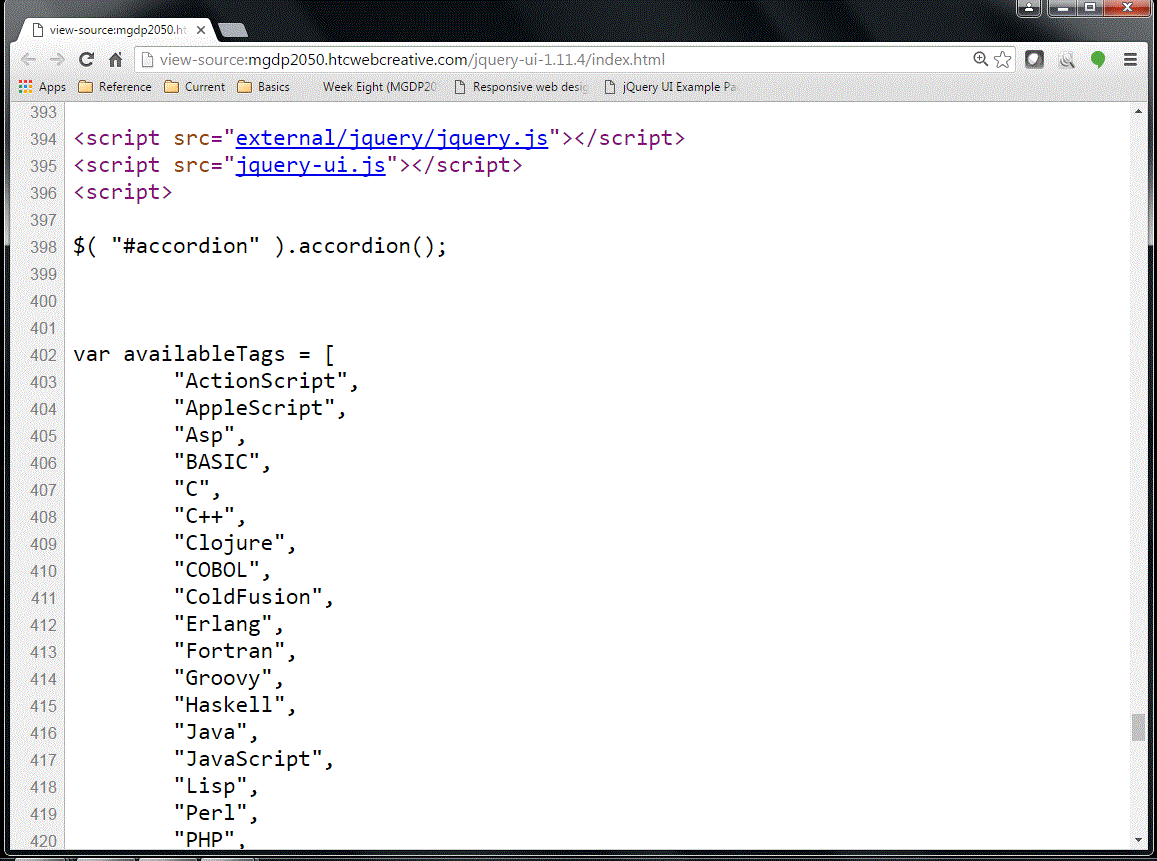
Instructor's example: JavaScript
The screenshot below shows some of the JavaScript for the instructor's Sample components page.
Note the external JavaScript files, and some internal JavaScript (only first portion shown here).
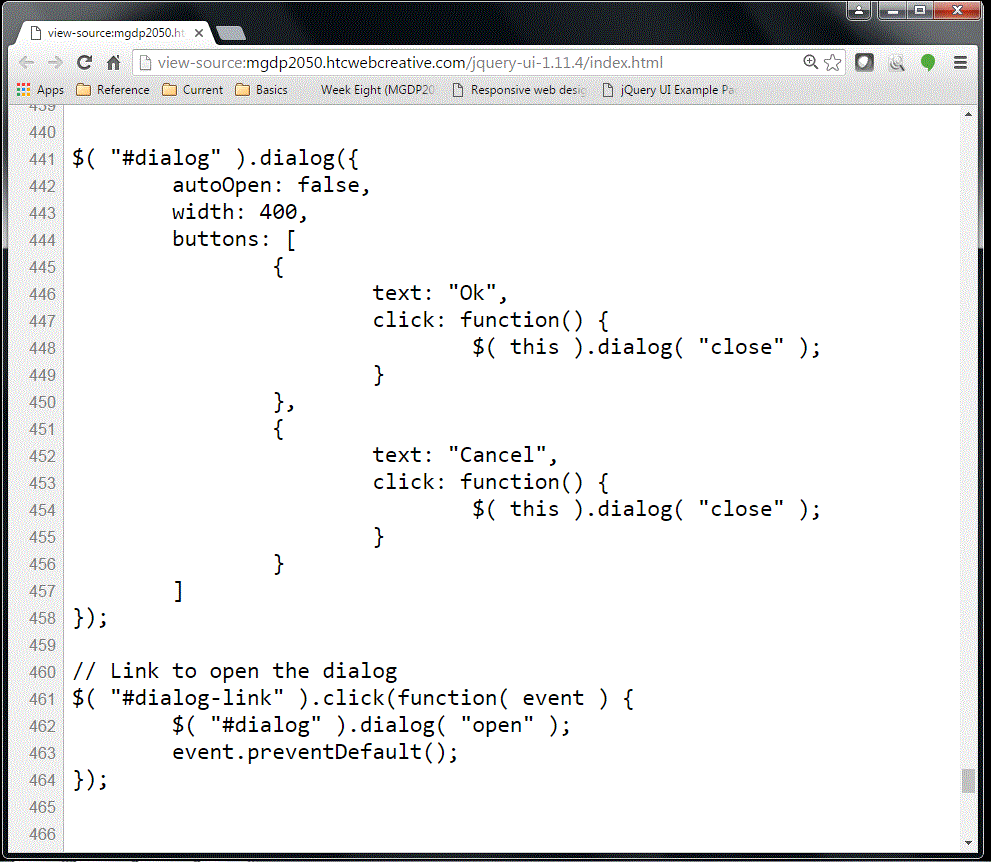
Instructor's example: Dialog component screenshot
The screenshot below shows the internal JavaScript for the Dialog component example:
Instructor's example: Dialog component text
Here is the JavaScript for the Dialog box:
$( "#dialog" ).dialog({
autoOpen: false,
width: 400,
buttons: [
{
text: "Ok",
click: function() {
$( this ).dialog( "close" );
}
},
{
text: "Cancel",
click: function() {
$( this ).dialog( "close" );
}
}
]
});
// Link to open the dialog
$( "#dialog-link" ).click(function( event ) {
$( "#dialog" ).dialog( "open" );
event.preventDefault();
});
Create folder named week8
In your local root folder, create a new folder named week8.
Create web page
In your week8 folder, create a web page named index.html.
- Similar to other exercise pages.
- Set page title, etc.
Demonstrate a jQuery UI component
In your web page, demonstrate a jQuery UI component of your choice.
Instructor's example, the Dialog component
- ...
Based on this demo:
Update your home page
On your Home page, make a link to your jQuery UI exercise.
Upload to web server
Upload your work to the web server:
- Exercise page
- jQuery UI folder
Exercises: for next week
Demonstrate two more jQuery UI components
Demonstrate two more jQuery UI components of your choice.
You may do this in the same web page, or you may create additional web pages.
- If you create additional web pages, provide links on your home page.